Research
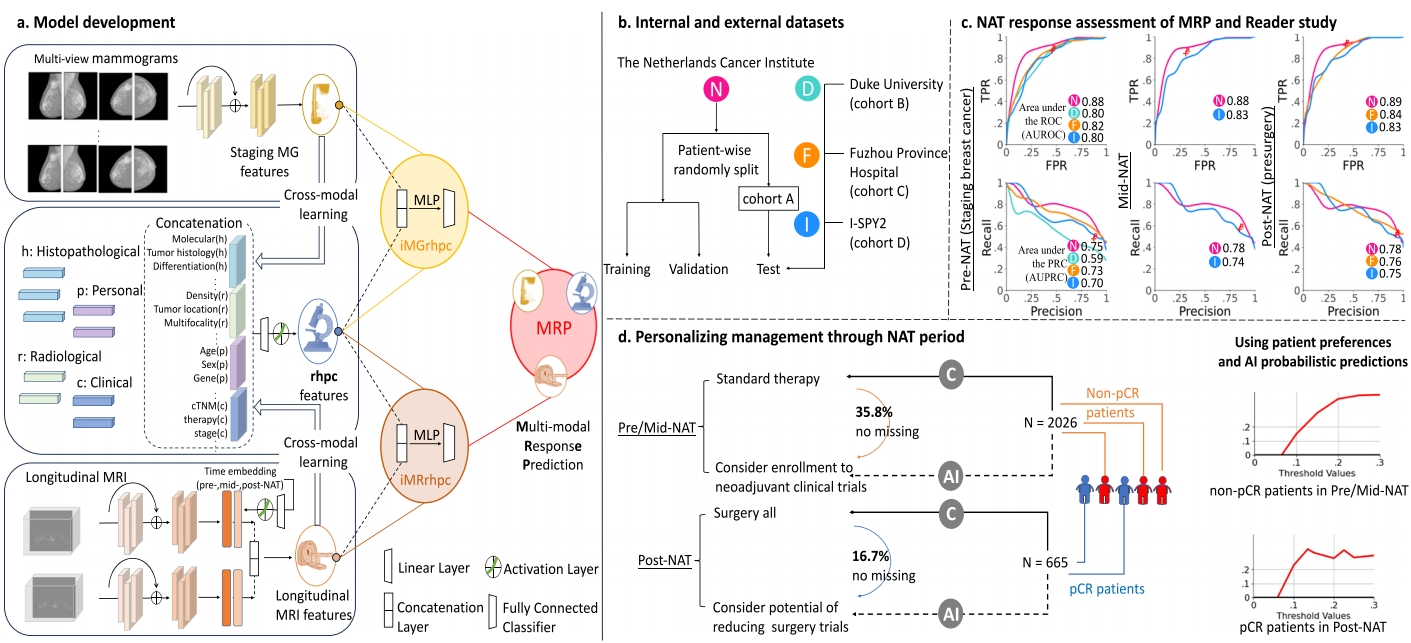
Breast Cancer Digital Twin
Breast Cancer Digital Twin
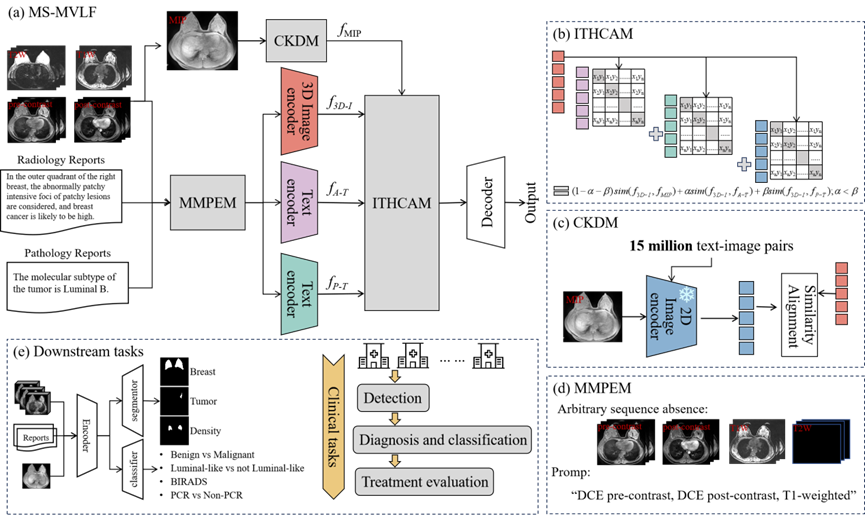
MS-MVLF: A Multi-Sequence Medical Vision-Language Framework with Cross-Dimensional Distillation for Enhanced Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
MS-MVLF: A Multi-Sequence Medical Vision-Language Framework with Cross-Dimensional Distillation for Enhanced Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
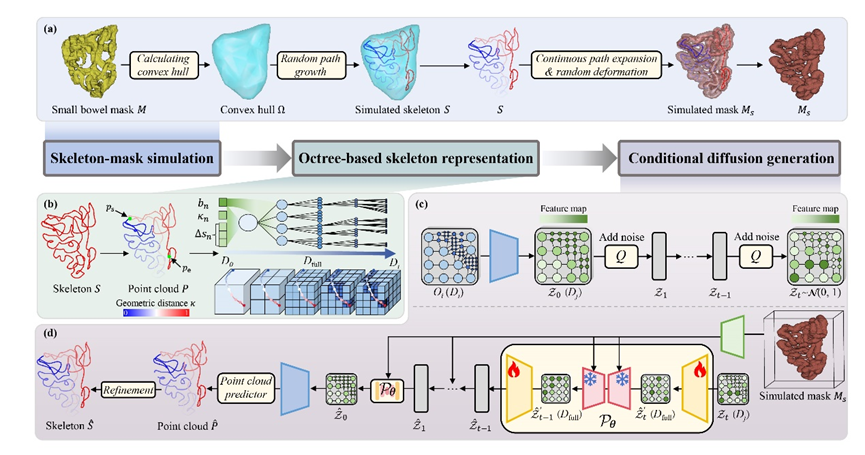
Tree-Diffusion_Octree-Based Conditional Diffusion Model for Small Bowel Skeleton Generation with Geometric Direction Modeling
Across four large-scale abdominal CT datasets, Tree-Diffusion achieves superior topological completeness, geometric accuracy, and generalization compared with prior skeletonization pipelines, while remaining efficient through sparse octree modeling.
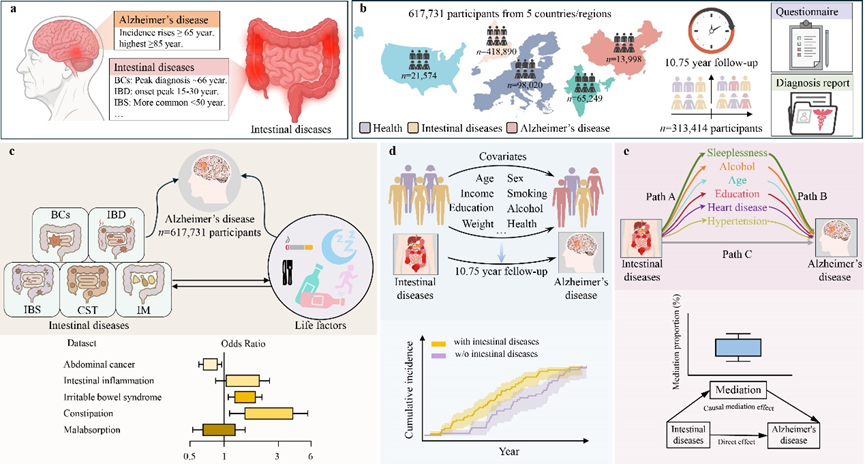
Intestinal diseases signal early Alzheimer’s disease risk across multi-country longitudinal cohorts
This work establishes a disease-anchored gut–brain biomarker strategy for early AD risk stratification—reusable, trackable, and scalable using routinely collected clinical records. By shifting part of risk assessment from resource-intensive neuroimaging to accessible gastrointestinal phenotypes (and their behavioral mediators), the project provides a pragmatic framework for population-level prevention, targeted follow-up, and earlier intervention planning.
IvyGPT: InteractiVe Chinese pathwaY language model in medical domain
General large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have shown remarkable success.
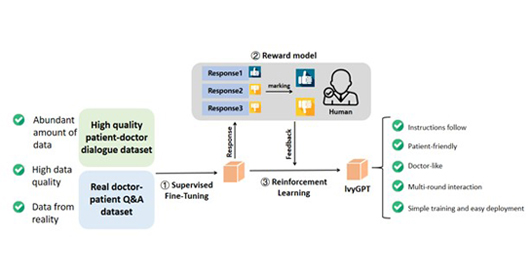
Image Quality Improvement of Mobile Ultrasound
Mobile ultrasound device suffer from low imaging quality due to hardware limitations. This research aims to improve the image quality by developing a deep learning-based algorithm, providing a more clear and high-quality ultrasound image.

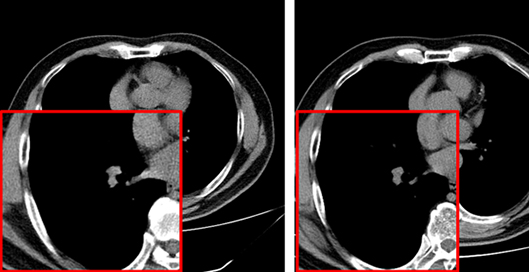
Chest CT-IQA: A Multi-Task Model for Chest CT Image Quality Assessment
In recent years, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic,a large number of Computerized Tomography (CT) imagesare produced every day for the purpose of inspecting lung diseases.
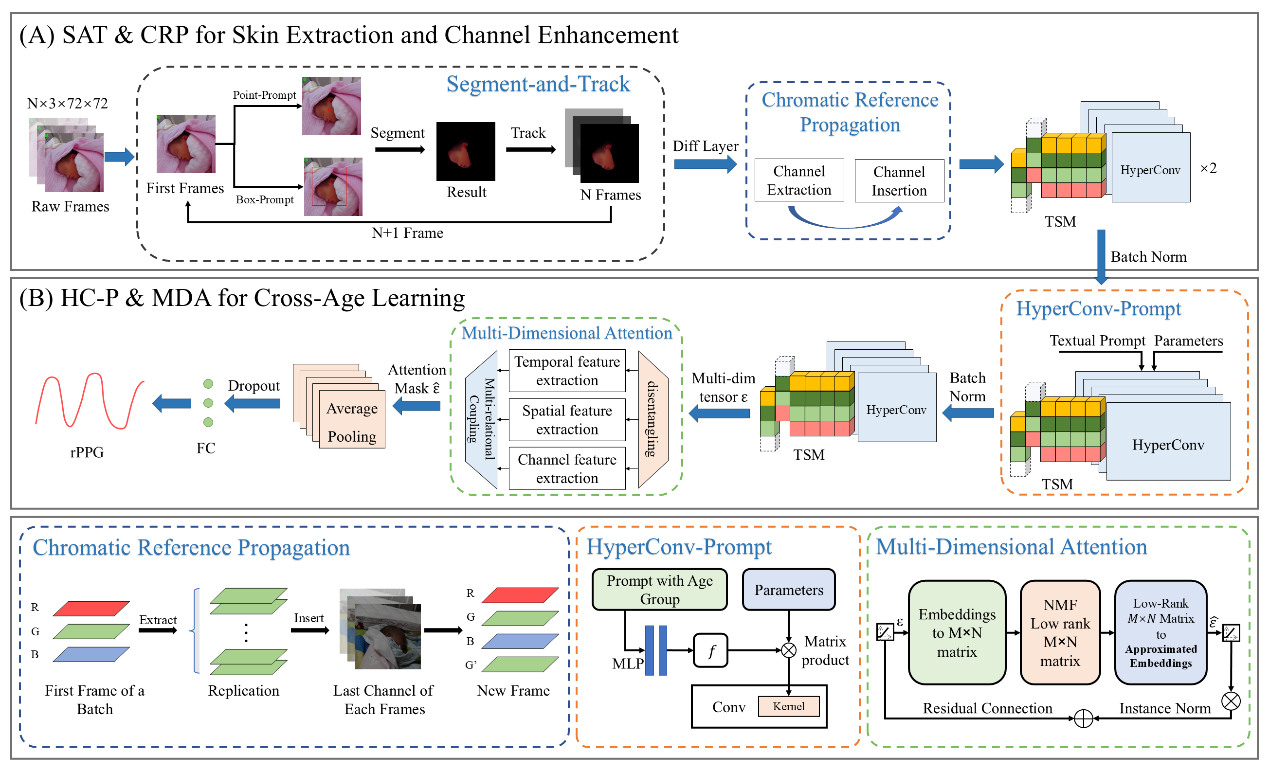
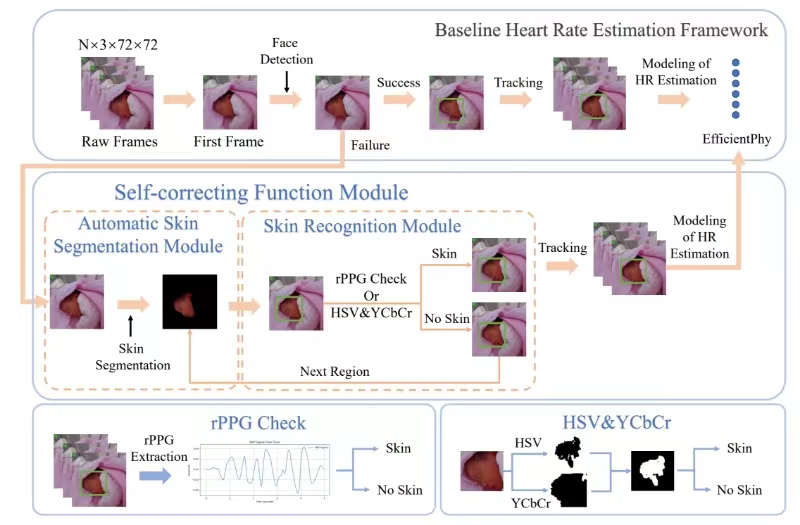
Video-based Physiological Monitoring with Age-Guided Enhancement
Remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) is a non-invasive method that monitors heart rate (HR) and other vital signs by detecting tiny color changes in the face caused by blood flow under the skin.
Automatic segmentation and direct calculation of radiotherapy
The quality of multi-focus microscopic image fusion hinges upon the precision of the image registration technology.

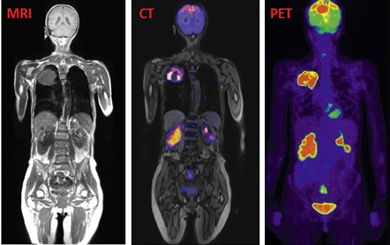
Nuclear Medicine Imaging Analysis
Nuclear medicine imaging uses radioactive tracers to reveal cellular physiology, providing key insights for diagnosis and treatment. It transcends traditional imaging by focusing on molecular activity, promoting personalized medicine.
Deep learning framework for microscope multi-focus images
A hybrid supervised fusion deep learning framework for microscope multi-focus images

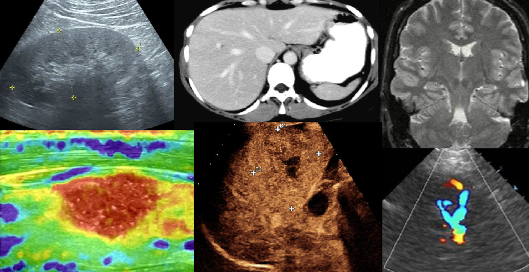
Multi-modality
Our research focuses on the intricate world of cross-organ, multi-modality imaging, delving into a diverse array of medical imaging techniques
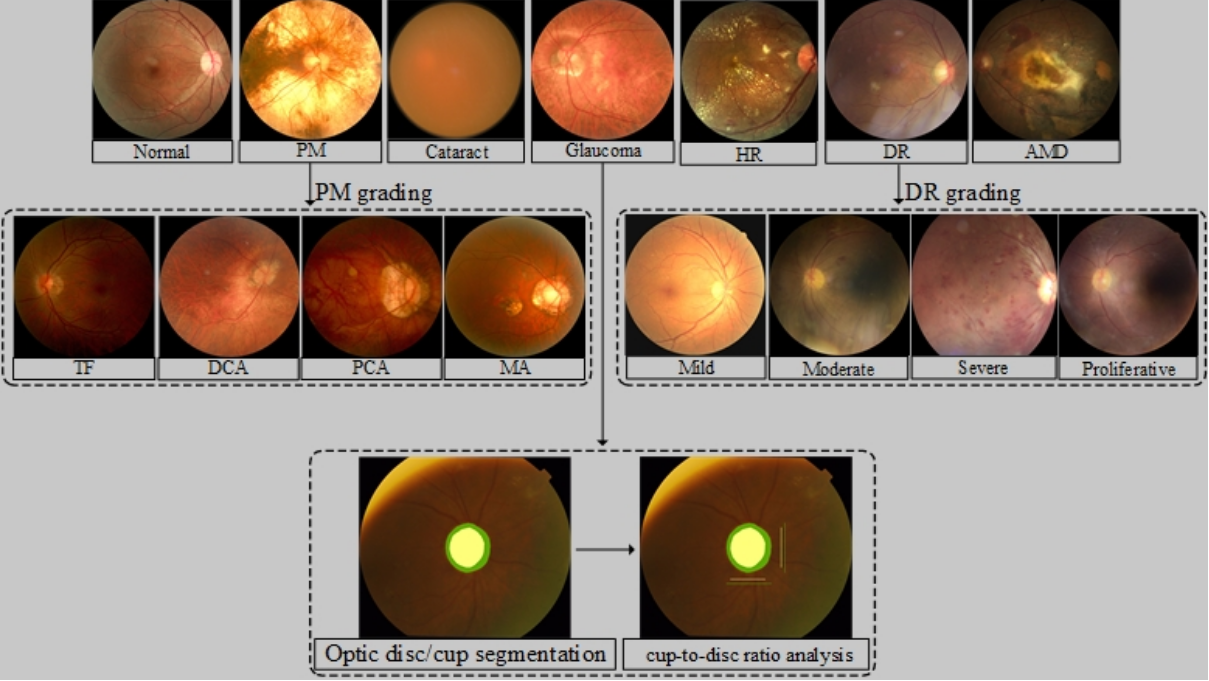
Application of AI algorithms in diagnosis of fundus diseases
The application of artificial intelligence algorithms in the diagnosis of retinal diseases is progressively leading the transformation of the field of medicine.
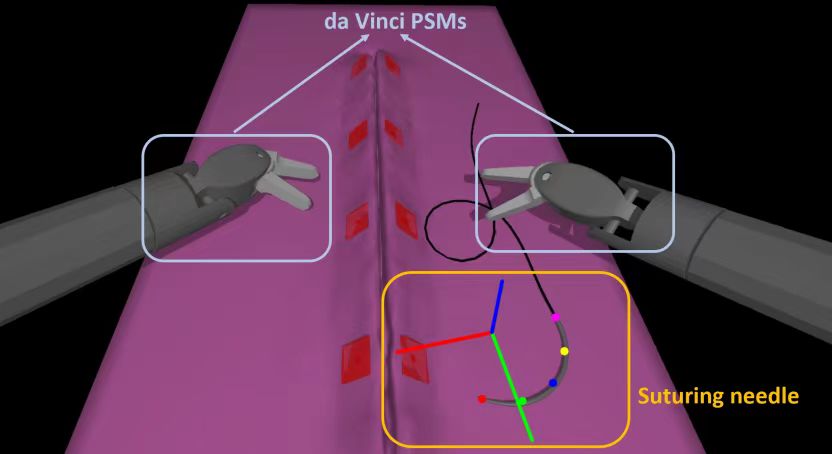
Da Vinci surgical robot
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) has ushered in a transformative era for minimally invasive procedures, with the DaVinci Surgical System at the forefront as a cutting-edge robotic surgical platform
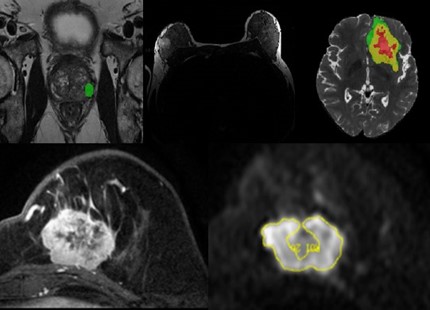
MRI Imaging Analysis
Analysis of MRI images included APTw imaging analysis and tumor segmentation, whole-genome analysis, and denoising.
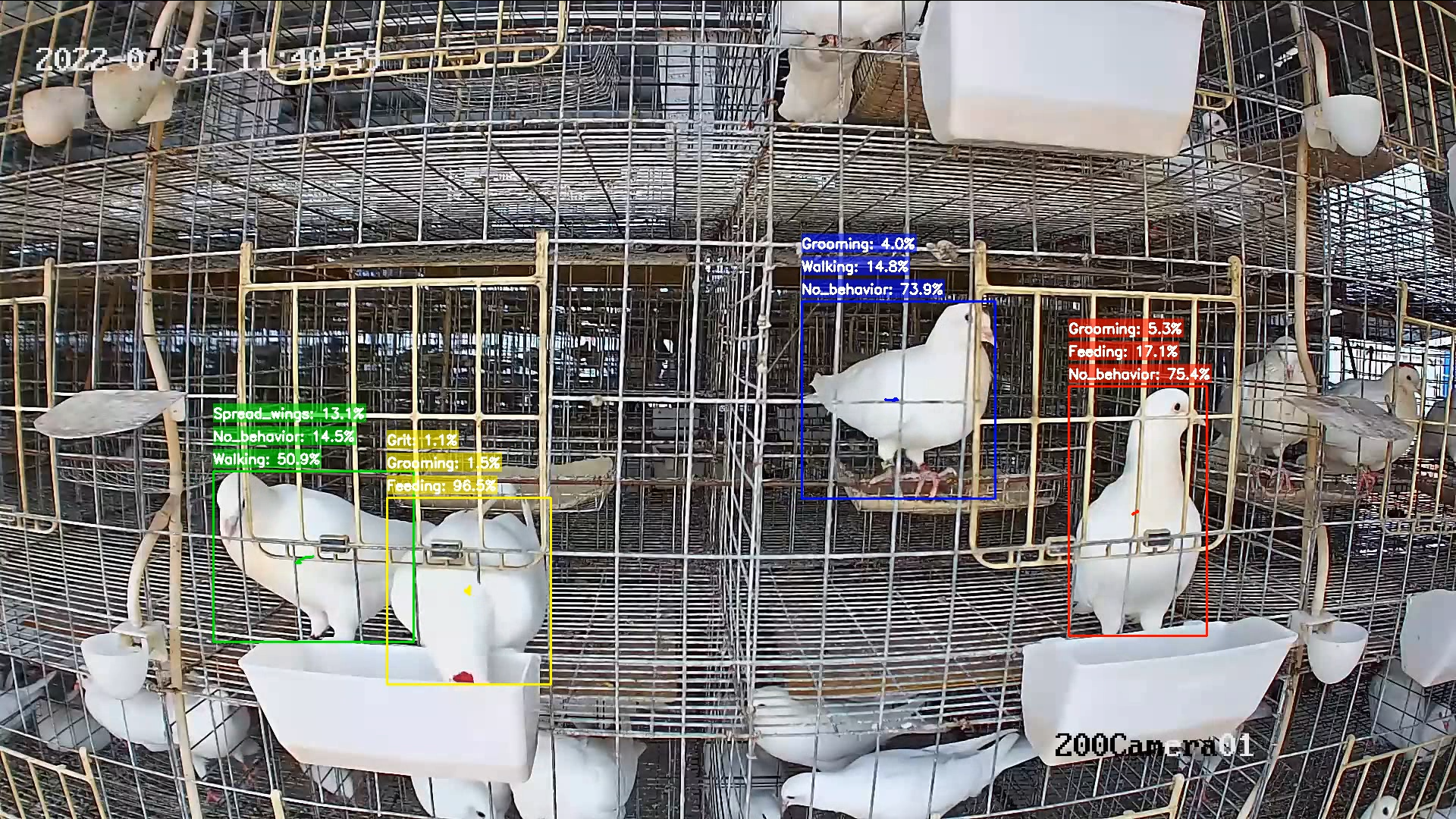
Video-based animal behaviour recognition
Traditional pigeon farming heavily relies on manual observation and experience-based judgment, making it difficult to monitor the health status of the flock and detect abnormal behaviors in real-time.
PCB Circuit Board Defect Detection
Efficient PCB defect detection is vital for maintaining high-quality and reliable electronic devices, leading to benefits such as improved product quality, cost reduction, regulatory compliance, brand reputation, and enhanced device lifespan. Additionally, it enhances market competitiveness by meeting industry standards.

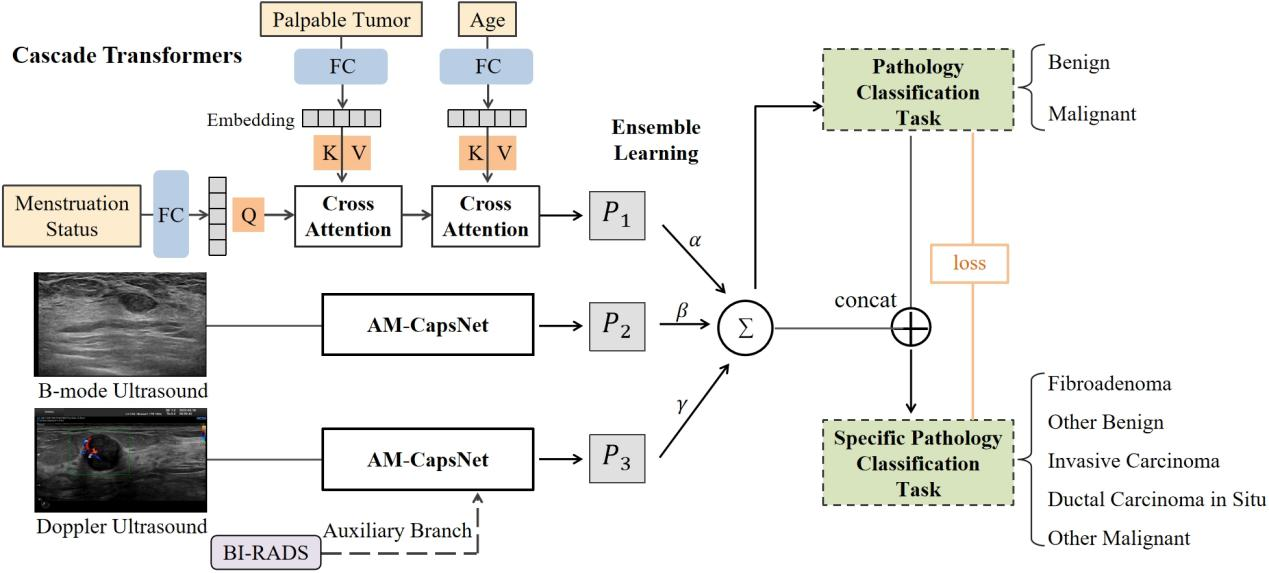
Risk prediction of breast cancer
The study of breast dense tissue is of great significance for the evaluation of breast health, the early detection of breast diseases and the risk assessment of breast cancer
Universal Ultrasound Model
Ultrasound imaging is widely utilized in clinical settings due to its cost-effectiveness, mobility, and safety. While current research in medical universal AI predominantly focuses on language models and general image segmentation, our study introduces a novel universal framework tailored specifically for ultrasound applications

Anatomy-aware Unified Model for MR-imaging-only Radiotherapy
In radiation therapy planning, CT images provide crucial tissue electron density information for dose calculation. However, CT scans expose patients to additional radiation. Although MRI images do not produce radiation, their unique signal characteristics require precise mapping to corresponding CT manifestations to ensure the effectiveness and safety of treatment. Therefore, generating high-quality pseudo-CT images from specific organ MRI data is of significant importance.
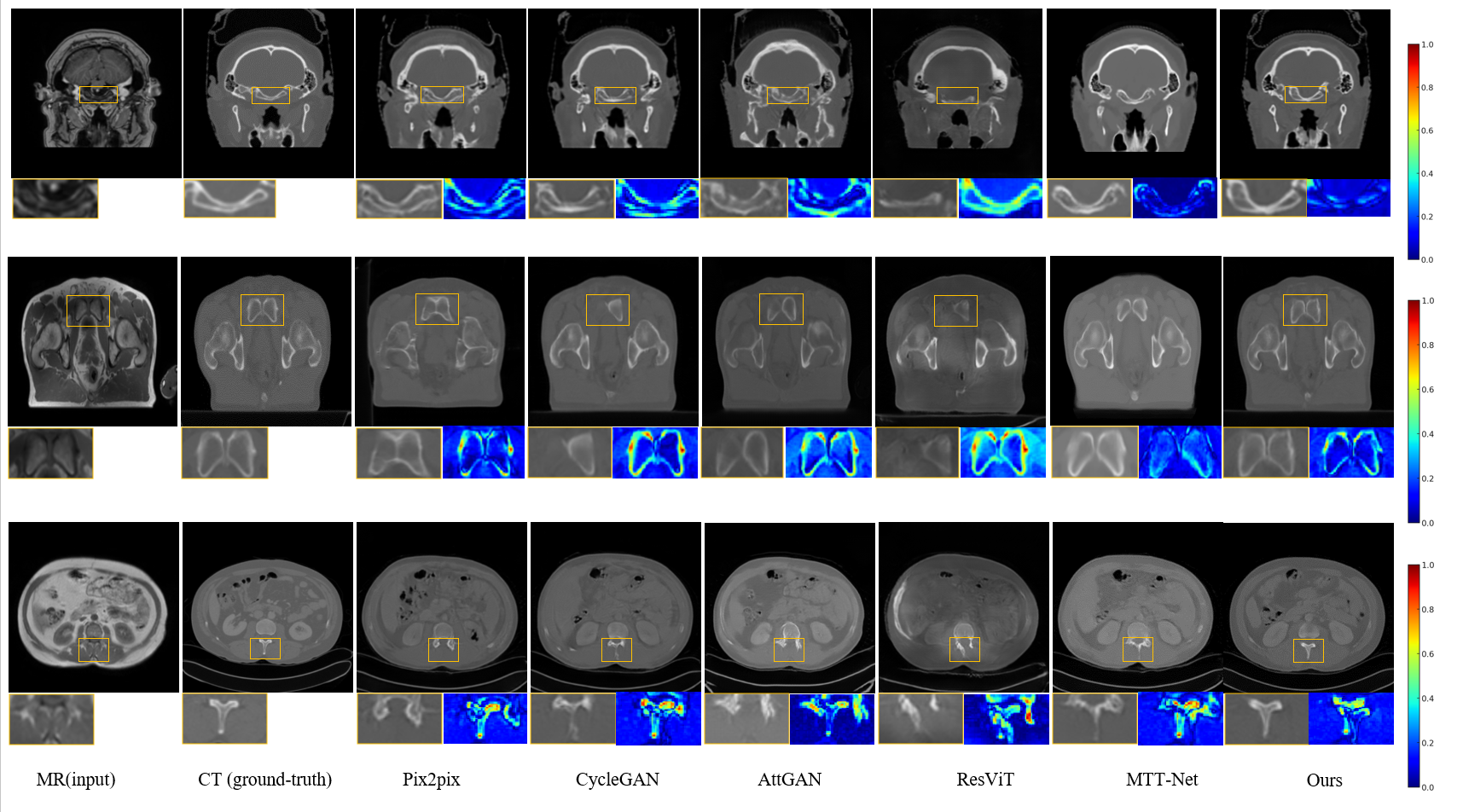
Automatic Detection of Breast Lesions in Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound with Cross-Organ Transfer Learning
This research highlights the potential of transfer learning and contrastive learning in enhancing CAD performance for breast cancer detection

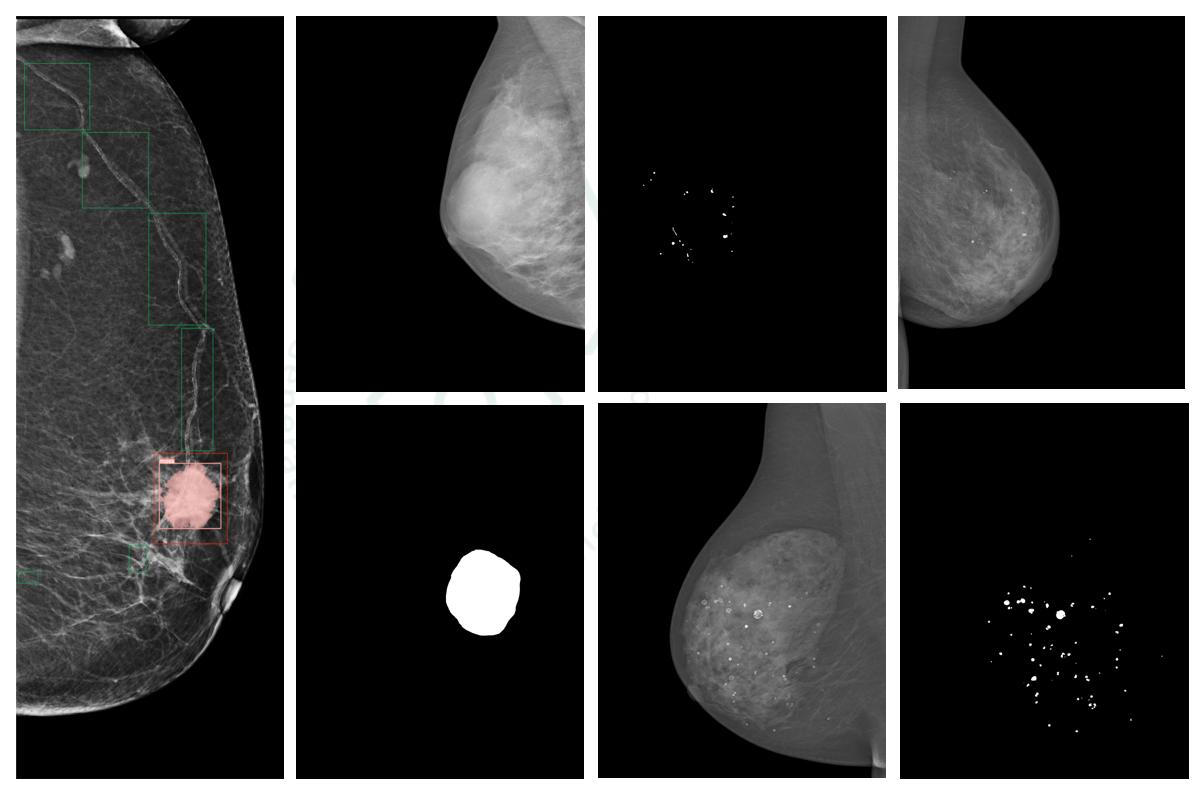
AI-Enhanced Mammogram Analysis: Precision in Breast Calcification and Mass Segmentation
Breast cancer claims many lives annually. Early and accurate detection via AI-enhanced mammography improves diagnosis of calcifications and masses, easing radiologists' workloads and boosting patient survival rates. Our project uses a modified U-Net model
Unsupervised Active Learning for Efficient Annotation
In real-world applications, the performance of artificial intelligence models often declines when there are discrepancies between training data and the data encountered in deployment environments—a challenge commonly known as domain shift. This issue is particularly critical in data-sensitive fields such as medical imaging, where collecting and labeling new domain-specific data is costly and time-consuming.
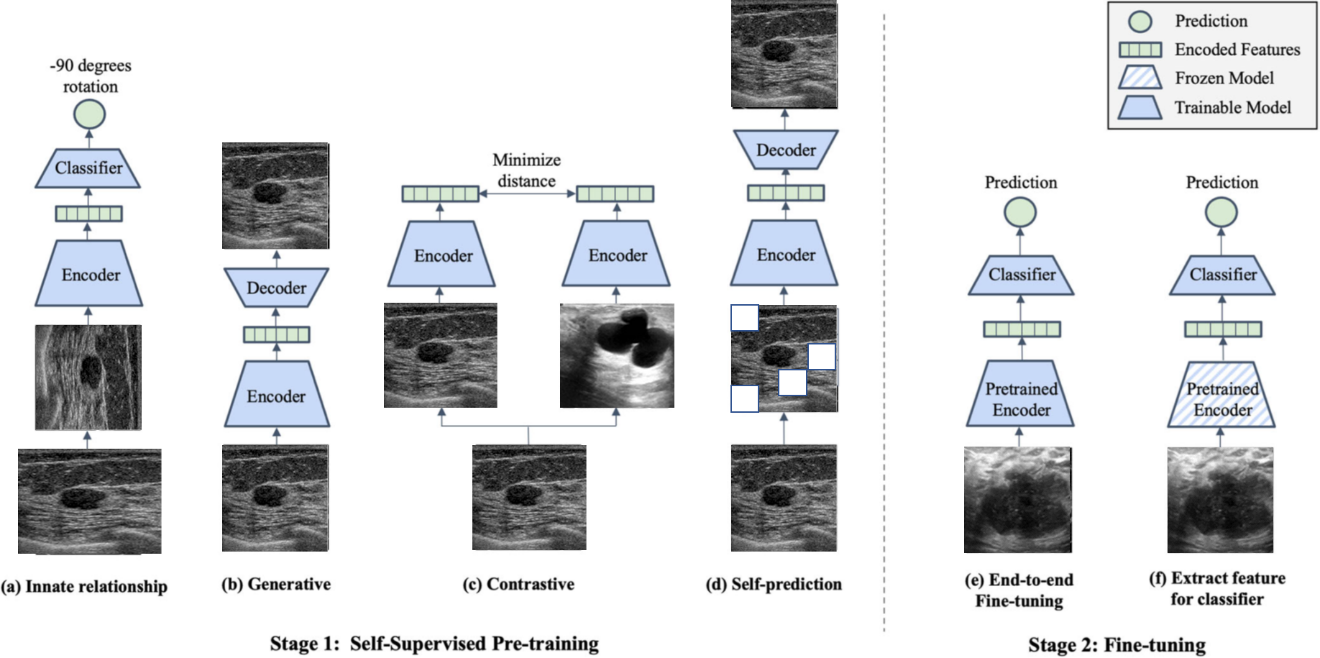
Breast Ultrasound Detection Based on Self-supervised Learning using Large-scale Datasets
Advancements in deep learning and computer vision provide promising solutions for medical image analysis, potentially improving healthcare and patient outcomes.Self-supervised learning has the potential to make significant contributions to the development of robust medical imaging models through its ability to learn useful insights from copious medical datasets without labels.
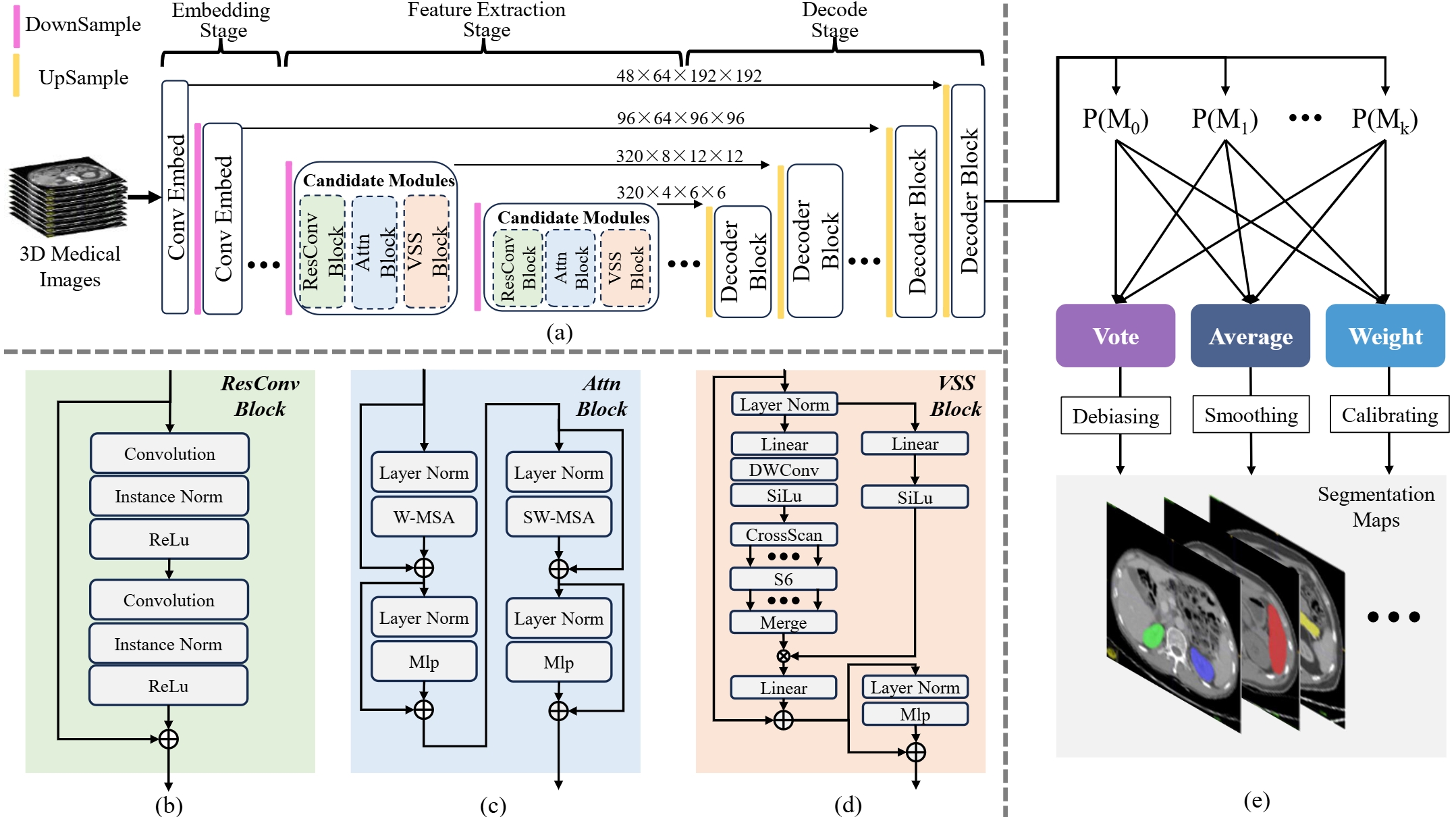
Bridging Model-Specific Gaps in 3D Medical Image Segmentation via Adaptive Multi-Model Ensemble of Complementary Architectures
3D medical image segmentation is pivotal in both academic and engineering domains. nnUNet, a recent deep learning-based innovation, has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance.
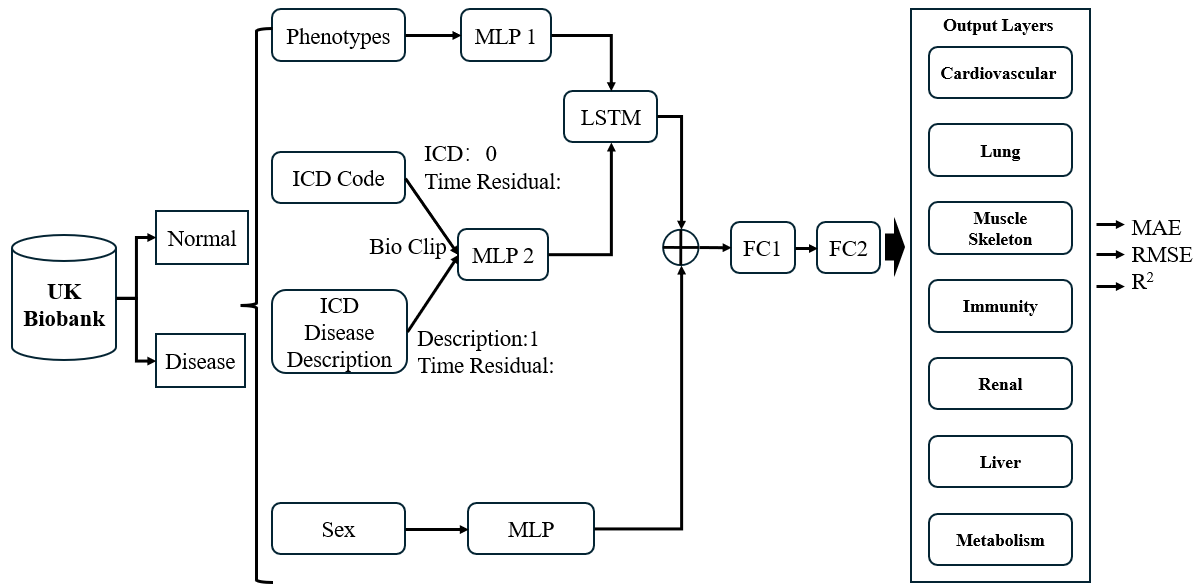
Using Electronic Medical Records to Predict Physiological Age as a Biomarker to Predict Geriatric Diseases
With the increasing of population aging, aging research has gradually become an important subject in the biomedical field. Human aging is not only the accumulation of physiological changes, but also the precursor of many diseases. Therefore, in-depth research on the aging process is of great significance for early disease prevention and health management.
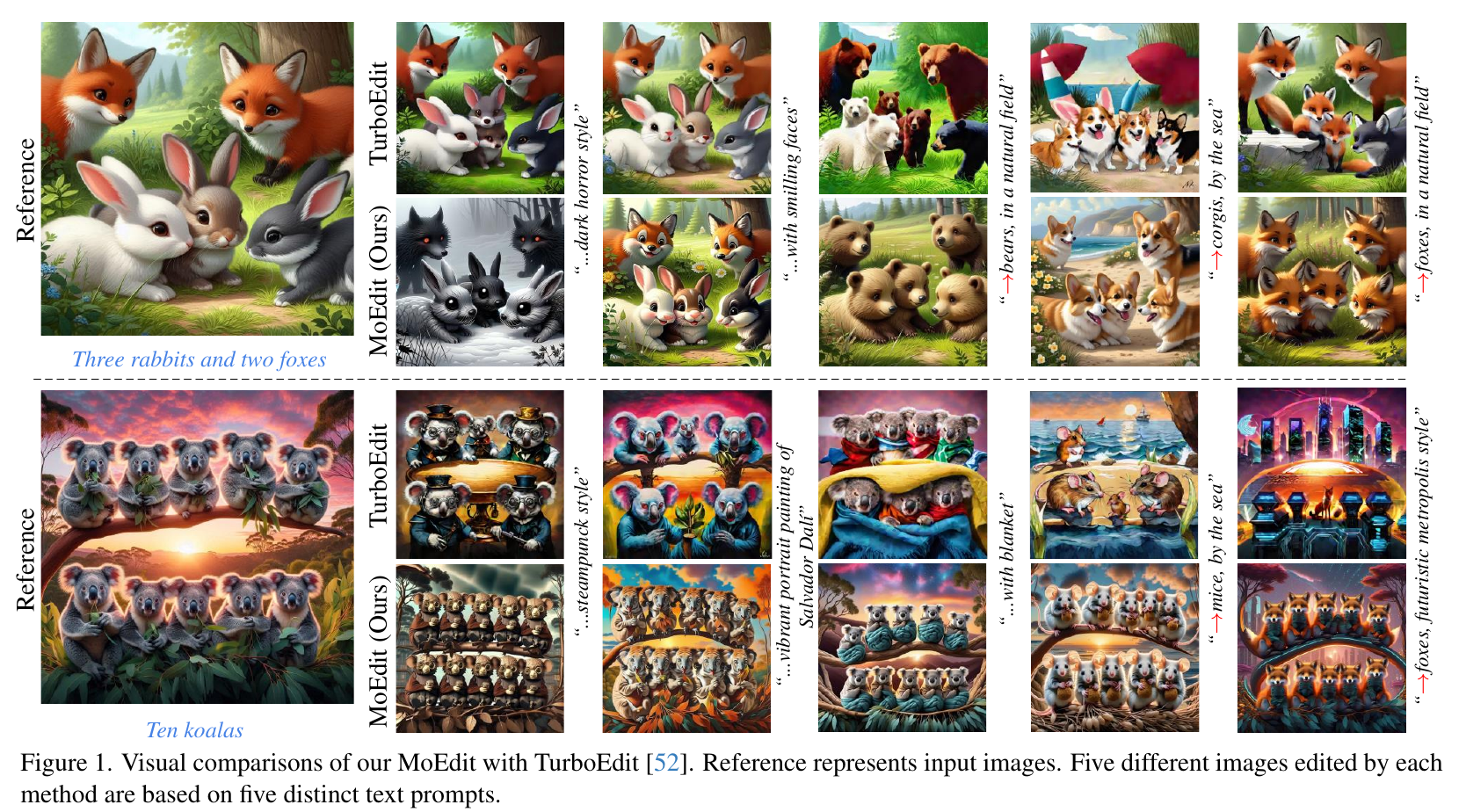
Artificial Intelligence Generated Content
Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) is a hot research direction in the field of artificial intelligence. Our team is dedicated to exploring the applications of AIGC technology in computer vision and graphics.