Linzehui, a doctoral student at the school of Applied Sciences of the Macao Polytechnic University, and other members of the research team, in conjunction with Case Western Reserve University, Shenzhen Institute of advanced technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sun Yat sen University, Shenzhen University and Shenzhen duying Medical Technology Co., Ltd., have successfully developed a universal ultrasonic AI framework called perceptguide. The framework innovatively introduces the "orchestration learning" paradigm, and realizes high-precision lesion segmentation and classification of ultrasound images of various organs (such as breast, thyroid, heart, liver, etc.) through the guidance of multi-dimensional prompt words.
This breakthrough research achievement has been received by medical image analysis, a top journal in the field of medical image computing (with an impact factor of more than 10), which marks the transition of ultrasound AI from the era of "specialized model" to the era of "universal framework", and provides a potential solution for the deployment and application of clinical AI
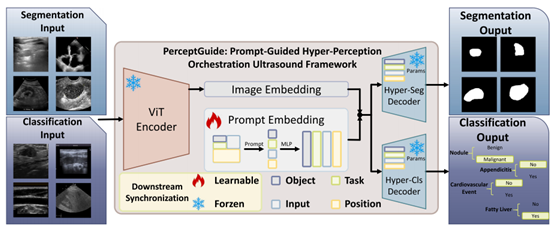
In clinical diagnosis, ultrasound is widely used in the examination of multiple organs because of its non-invasive, portable and real-time characteristics. However, the ultrasound images of different organs have great differences in texture, structure and artifacts, which leads to the traditional AI model can only be "disease specific", that is, a model can only deal with one organ or one task (such as only segmentation or classification). If we want to deploy AI auxiliary diagnosis covering multiple organs in clinic, we need to develop and maintain dozens of independent models, which is not only expensive to calculate, but also complex and difficult to expand.
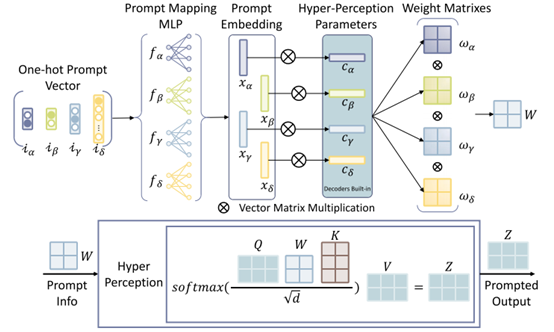
To meet this challenge, perceptguide came into being. It is a unified and automatic learning framework, which can flexibly process images from 16 public datasets of 9 different organs in a single model, and simultaneously perform the two core tasks of segmentation and classification. Its core innovation lies in a "hyper perception module" guided by cue words. The module can understand four key words: object, task, input and position, and dynamically adjust the internal attention mechanism of the model according to these instructions, so that it can focus on the most critical image features for different scenes like an experienced doctor.
The perceptguide framework mainly has the following four technological innovations:
General multi organ and multi task framework: for the first time, a single model is implemented to deal with the segmentation and classification tasks of nine different organs. Its comprehensive performance significantly exceeds that of the specialized model trained separately for each organ, while significantly reducing the total number of parameters and complexity of model deployment.
Super perception module guided by cue word: the original cue word mechanism gives the model unprecedented flexibility. The doctor or system only needs to give simple instructions (such as "classify thyroid nodules"), and the model can automatically call the corresponding prior knowledge to accurately complete the task.
Downstream synchronization technology of attention matching: for new data or new tasks that may appear in the future, the framework designs an efficient fine-tuning scheme. It only needs to update a few parameters related to the prompt word to quickly adapt to the new data, which greatly improves the generalization ability and scalability of the model.
Building a large-scale multi center benchmark data set: the team has integrated and standardized 16 public ultrasound data sets, and built the largest public multi task, multi organ ultrasound data set M ² -us, which provides a valuable benchmark platform for the follow-up study of general ultrasound AI.